Thyroid
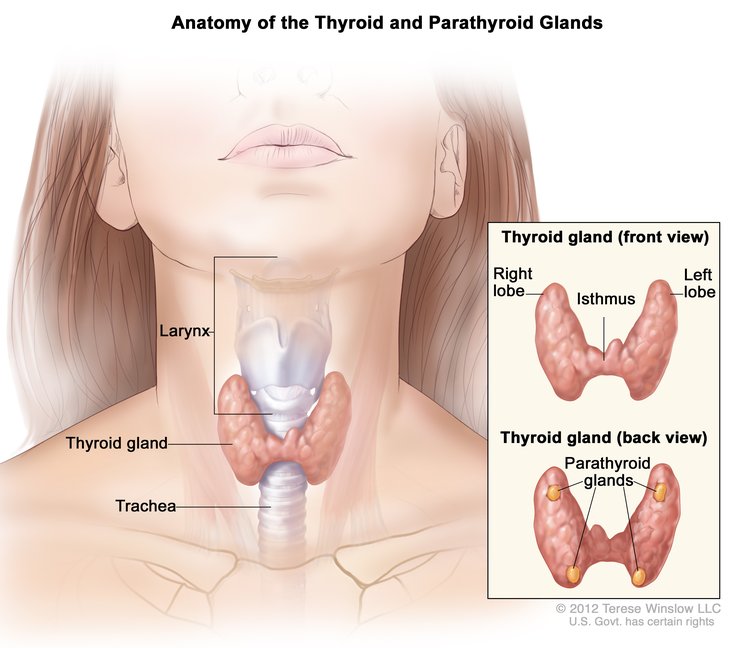
The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid is an endocrine gland in the throat, and consists of two linked lobes. It is found at the front of the neck, below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones, which influence the metabolic rate, protein synthesis, and have a wide range of other effects, including on improvement. The thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are synthesized from tyrosine and iodine. The thyroid also produces calciton in, which plays a main role in calcium homeostasis.
Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted from the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) created by the hypothalamus.
What Are Thyroid Problems?
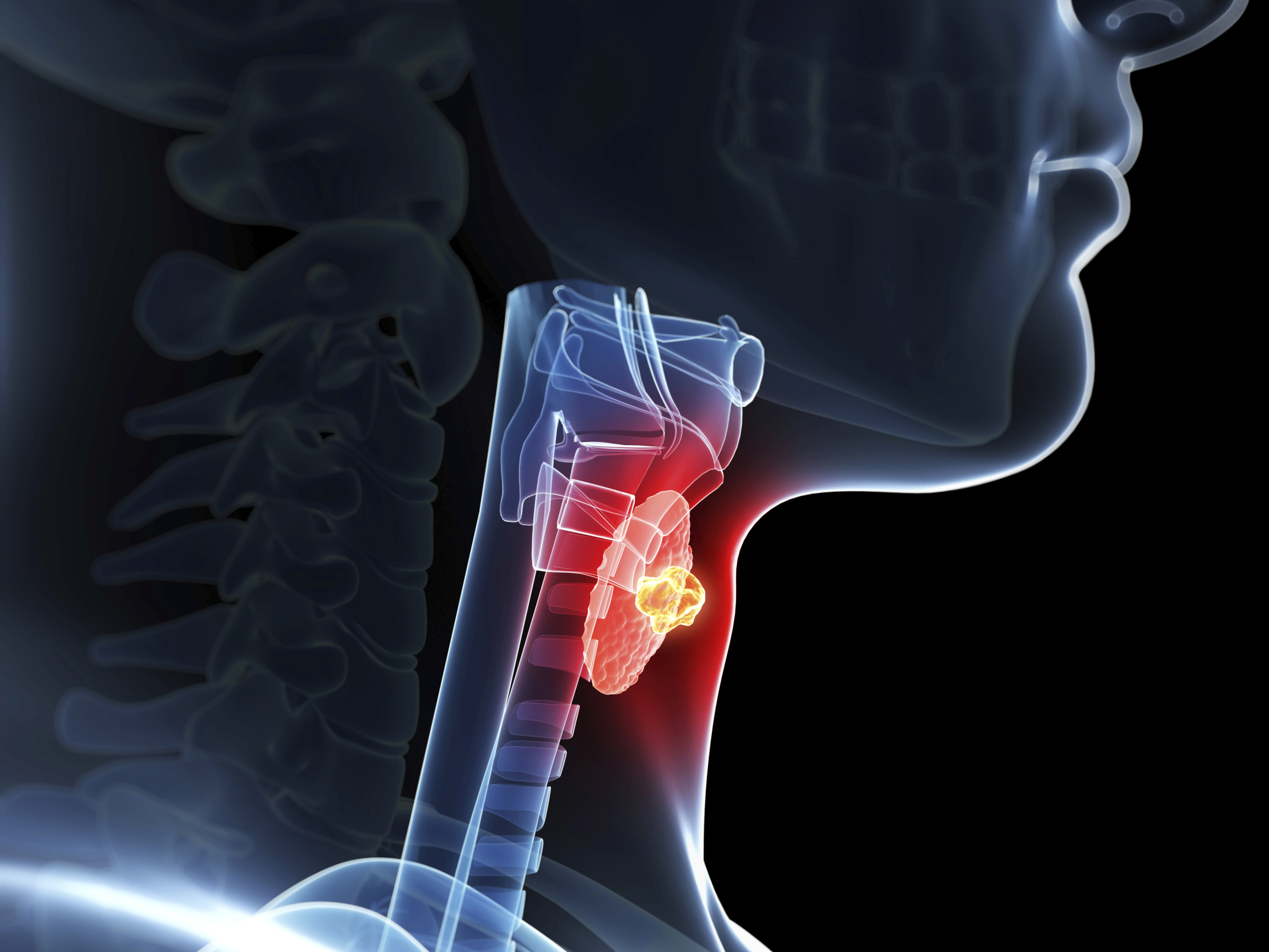
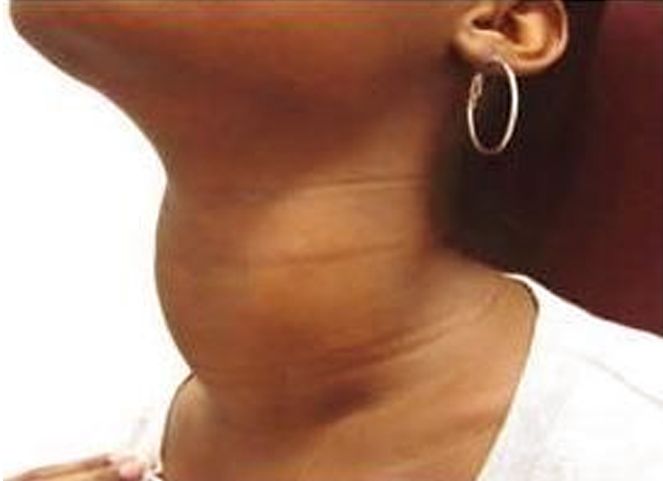
Through the hormones it produces, the thyroid gland influences nearly all of the metabolic processes in your body. Thyroid disorders can range from a small, safe goiter (enlarged gland) that needs no treatment to life-threatening cancer. The most general thyroid problems involve abnormal production of thyroid hormones. Too much thyroid hormone results in a situation known as hyperthyroidism. Insufficient hormone creation leads to hypothyroidism.
Although the effects can be unpleasant or uncomfortable, most thyroid problems can be managed well if properly diagnosed and treated.
What Causes Thyroid Problems?
All types of hyperthyroidism are due to an overproduction of thyroid hormones, but the situation can occur in several ways:
- Graves’ disease: The production of too much thyroid hormone.
- Toxic adenomas: Nodules increase in the thyroid gland and start to secrete thyroid hormones, upsetting the body’s chemical balance, some goiters may include several of these nodules.
- Sub-acute thyroid: It is Inflammation of the thyroid that causes the gland to “leak” excess hormones, resulting in temporary hyperthyroidism that commonly lasts a few weeks but may persist for months.
Causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Hashimoto’s thyroid: In this autoimmune disorder, the body attacks thyroid tissue. The tissue ultimately dies and stops producing hormones.
- Removal of the thyroid gland: The thyroid may have been surgically removed or chemically destroyed.
- Lithium: This drug has also been implicated as a cause of hypothyroidism. Untreated for long periods of time, hypothyroidism can bring on a myxedema coma, a rare but potentially critical condition that requires instant hormone treatment.
Hypothyroidism poses a special risk to newborns and infants. A lack of thyroid hormones in the system at an early age can lead to the improvement of cretinism (mental retardation) and dwarfism (stunted growth). Most infants now have their thyroid levels checked routinely soon after birth. If they are hypothyroid, treatment starts immediately.
In infants, as in adults, hypothyroidism can be due to these causes:
- A pituitary disorder
- A defective thyroid
- Lack of the gland entirely
What is the thyroid?
Your thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland found at the base of your neck, just below your Adam’s apple. This gland makes thyroid hormone that travels in your blood to all parts of your body. The thyroid hormone controls your body’s metabolism in many ways, including how fast you burn calories and how fast your heart beats.
How is hypothyroidism treated?
Hypothyroidism is treated with medicine that gives your body the thyroid hormone it needs to work normally. The most common medicines are man-made forms of the hormone that your thyroid makes. You will likely need to take thyroid hormone pills for the rest of your life. When you take the pills as your doctor tells you to, the pills are very safe.